Clinical Genomics Laboratory Services
We offer a range of genomic laboratory services to support drug discovery, precision medicine and clinical development. Our industry-leading team advances research by delivering scientific insights that help clients maximize the value of their data.
Clinical Genomics Laboratory Services
We offer a range of genomic laboratory services to support drug discovery, precision medicine and clinical development. Our industry-leading team advances research by delivering scientific insights that help clients maximize the value of their data.

Clinical Genomics Laboratory Services
Next Generation Sequencing Services
Microsatellite Instability Assay
Immune Landscape Signatures
Oncomine Precision Assay
Tumor Mutational Burden
TruSight Oncology 500 (TSO500)
TruSight Oncology 500 ctDNA
Whole Exome Sequencing
Liquid Biopsy ctDNA
TruSight Oncology 500 ctDNA
Single Cell and Spatial Genomics
Single Cell RNA Sequencing
Spatial Genomics
Biomarker Discovery
Technology Platforms
Bioinformatics Services
Ordering and Client Login
Central Laboratory Services
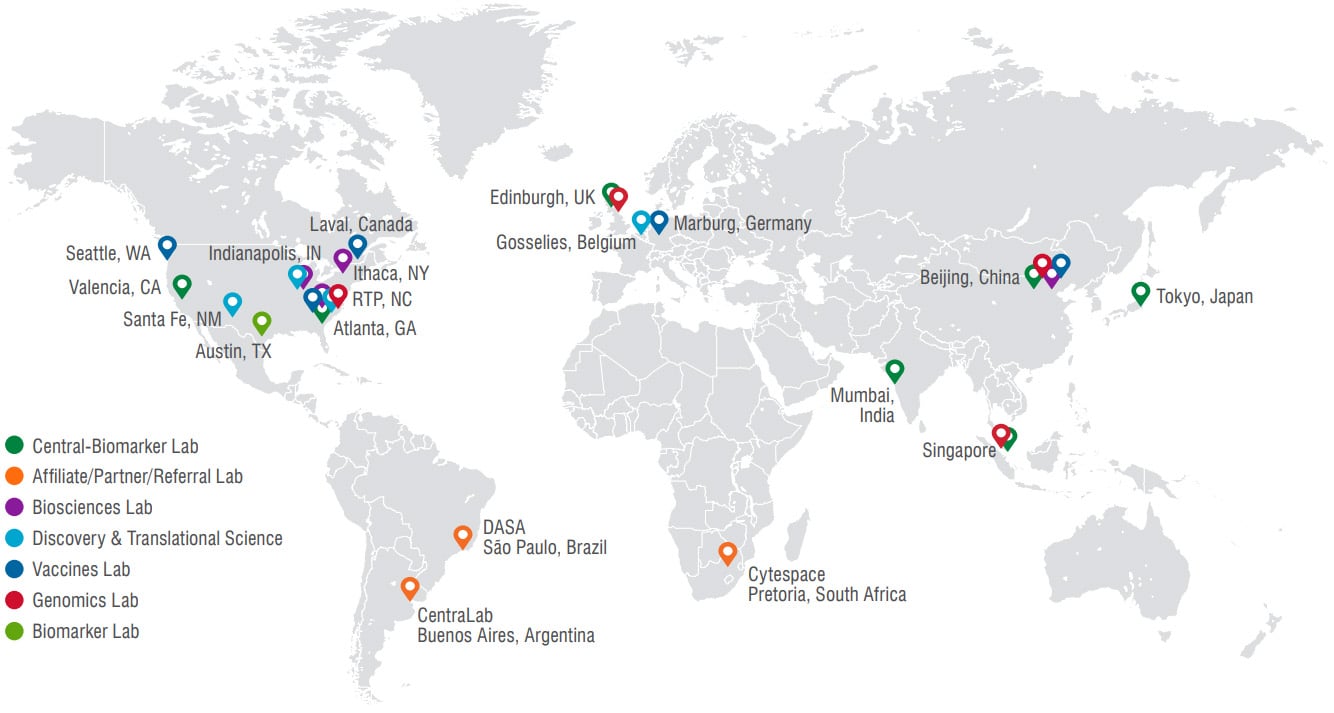
Q2 Solutions Genomics has four laboratory locations.

| SERVICE | CAPABILITIES | LOCATION AVAILABILITY | |||
| USA | CHINA | UK | SINGAPORE | ||
| Anatomic pathology |
|
|
|
|
|
| Isolations |
|
|
|
|
|
| Whole human genome sequencing |
|
|
|
|
|
| DNA exome sequencing |
|
|
|
||
| RNA sequencing |
|
|
|
|
|
| Targeted sequencing |
|
|
|
|
|
| Thermo Fisher sequencing |
|
|
|
|
|
| Single cell RNA sequencing |
|
|
|||
| Spatial RNA and protein profiling |
|
|
|||
| PCR assays |
|
|
|
||
| NanoString nCounter panels |
|
|
|
||
| Bioinformatics |
|
Centralized in RTP | |||
Regulatory standards
| Our Quality Management System (QMS) is based upon the standards set forth in Good Clinical Practices (GCP), College of American Pathologists (CAP) and Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA). | |
| CAP | CAP Accreditation since 2017 |
| CLIA (USA only) |
CLIA Certified since 2010 |
| CLIA (Edinburgh) | CLIA Certified since January 2024 |
| GCP | Q2 Solutions maintains a QMS that is compliant to the applicable Good Clinical Practices for clinical and genomic testing conducted |
| NYS (USA only) |
NYS certified since 2018 |
100,000samples isolated andsequenced annually |
75+assays |
40+sequencing platformsin operation globally |
90+bioinformaticians andsoftware developers |
Related Services & Solutions
Related Thought Leaders Insights
Single-Cell RNA Profiling of FFPE Tissues
Single-cell RNA-seq has faced a limitation in the past, as viable cells from fresh or cryopreserved solid tumor biopsies were required, preventing the use of ubiquitous formalin-fixed,...
Evaluation and Reproducibility Study using NanoString GeoMx Immune Pathway Panel
The rapidly advancing field of spatial biology has led to development of new platforms which provide measurements of gene and protein expression and their precise localization to defined tissue...
Bioinformatics and Computational Solutions for Genomic Insights
With over 500 years cumulative expertise in genomics, bioinformatics, and information technologies, we provide infrastructure and consultative services to enable you with the fastest path from sample...